本文最后编辑于 前,其中的内容可能需要更新。
小声bb + 一些吐槽
下面先bb一些概念性的东西,虽然部分是copy的,但是整理到一起看起来知识点不是那么散,那些上来就哔哔怎么用怎用的博客文章是真没意思,关键写的还不咋的,要么就说的乱七八糟除了他自己没人看得懂,要么就依赖一大堆,搞个Feign的demo还扯那微服务的东西一大堆,依赖Eurake和微服务环境,单独使用不行?除了cv多少带点思考吧。
相信能看到这篇文章的看客们(可能并没有),多多少少听过微服务的一些概念,也知道Feign能干啥,虽然我也不是特别懂,但我还是会把知识点发散开来,本文就当做一篇随时可以巩固的文章,新手也可通过本文入门。
啥是“声明式服务调用”
可以从编程范式入手了解,常见的编程范式有:
- 命令式编程(Imperative Programming)
- 声明式编程(Declarative Programming)
- 函数式编程(Funational Programming)
- 面向对象编程(Object-oriented Programming)
>>> 声明式编程范式:声明式编程表明想要实现什么目的,应该做什么,但是不指定具体怎么做。
这里有一篇笔者认为关于编程范式的不错的文章,可以拓展一下眼界:【CSDN】编程范式(author:一位Python高级开发工程师)
那么我们简单理解一下声明式服务调用:声明调用的URL地址,请求方式,和返回结果,但具体如何调用交给底层实现.
为什么要使用声明式服务调用?
- 对系统使用方,通过设计声明式的接口,开发者无需关心底层实现,而更多的关注上层业务
- 对系统实现方,通过声明式的接口,上层使用者接口相对稳定前提下,系统可以不断的迭代优化
- 对整个系统而言,能够更系统的收集更多信息,能够依据策略进行系统行为优化,提升系统效率
使用Feign声明式web客户端,只需要声明一个接口即可,不需要关心传参、发送请求、获取响应内容、关闭连接等细节,Feign全部帮我们做好了。
SpringCloud集成了Feign组件,一个是 spring-cloud-starter-feign,一个是spring-cloud-starter-openfeign,前者已经过时。openfeign使得SpringCloud服务间调用变得更简单方便,但不是有SpringCloud才有Feign。
demo
这里我们以SpringBoot环境为例,使用SpringCloud的openfeign组件,哎,但是我们不是微服务环境,使用openfeign的原因是让系统配置少些,这段的主要目的是了解Feign的使用而不是配置。
maven关键配置
首先,maven依赖与版本,SpringBoot和SpringCloud版本定义如下
1
2
3
4
5
| <properties>
<spring-boot.version>2.3.4.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR1</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
|
openfeign的依赖不需要写版本
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
依赖管理块配置如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
|
Feign的服务提供与消费
idea中创建两个model,一个是普通的web项目,做服务提供者(下称提供端),一个做Feign的消费者(下称消费端)。
提供端provider模块配置:
配置文件如下,启动类正常的默认配置即可。
1
2
3
| spring.application.name=fegin-demo-provider
server.servlet.context-path=/provider
server.port=8080
|
消费端consumer模块配置:
配置文件省略,仅使用测试类测试service的bean即可。我们需要用到两个注解:
@EnableFeignClients开启Feign客户端的功能
启动类加上@EnableFeignClients注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication
public class FeignDemoConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FeignDemoConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
@FeignClient使一个接口成为Feign的客户端
1
2
3
4
| @FeignClient(name = "beanName", url = "http://ip:port/xxx", path = "/prefix")
public interface xxxService {
}
|
编码测试
为了能更好的展现出Feign的能力,服务提供可以大致分为几种情况进行测试:
- 返回值类型不同:基本类型(String、java基本数据类型的包装归为一类)、自定义引用类型(bean)、泛型等,见下文
- 参请求数位置不同:控制层方法常见的接收参数情况,请求头、请求体,url等等
- 出错情况:服务提供端响应为500或404或400等
- 其它非正常使用情况
先构建pojo类,提供端与消费端都要构建。
自定义引用类型 User
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
|
泛型,以常见的REST业务响应格式为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| @Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class MyResponse<T> {
private int code;
private String message;
private T data;
public static final int CODE_SUCCESSFUL = 0;
public static final int CODE_FAILED = -1;
public static final String MESSAGE_SUCCESSFUL = "successful";
public static final String MESSAGE_FAILED = "failed";
public static <T> MyResponse<T> successful() {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_SUCCESSFUL,MESSAGE_SUCCESSFUL,null);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> successful(T data) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_SUCCESSFUL,MESSAGE_SUCCESSFUL,data);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> successful(String message) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_SUCCESSFUL,message,null);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> successful(String message, T data) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_SUCCESSFUL,message,data);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> failed() {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_FAILED,MESSAGE_FAILED,null);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> failed(T data) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_FAILED,MESSAGE_FAILED,data);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> failed(String message) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_FAILED,message,null);
}
public static <T> MyResponse<T> failed(String message, T data) {
return new MyResponse<>(CODE_FAILED,message,data);
}
|
case1:返回值类型不同
1.1 基本类型、bean、泛型,JSONObejct、ResponseEntity(SpringWeb提供的响应体封装)
提供端web
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/type")
public class ProviderTypeController {
private static User admin = new User("admin",18);
@RequestMapping("/myResponse/string")
public MyResponse<String> returnMyResponseString() {
return MyResponse.successful(MyResponse.MESSAGE_SUCCESSFUL,"hello");
}
@RequestMapping("/myResponse/user")
public MyResponse<User> returnMyResponseUser() {
return MyResponse.successful(admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/user")
public User returnUser() {
return admin;
}
@RequestMapping("/int")
public Integer returnInteger() {
return 100;
}
@RequestMapping("/jsonObject")
public JSONObject returnJsonObject() {
String jsonText = JSON.toJSONString(admin);
return JSON.parseObject(jsonText);
}
@RequestMapping("/user")
ResponseEntity<User> returnResponseEntityUser();
}
|
消费端service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| @FeignClient(name = "consumerTypeService", url = "http://127.0.0.1:8080/provider", path = "/type")
public interface ConsumerTypeService {
@RequestMapping("/myResponse/string")
MyResponse<String> returnMyResponseString();
@RequestMapping("/myResponse/user")
MyResponse<User> returnMyResponseUser();
@RequestMapping("/user")
User returnUser();
@RequestMapping("/int")
Integer returnInteger();
@RequestMapping("/jsonObject")
JSONObject returnJsonObject();
@RequestMapping("/user")
ResponseEntity<User> returnResponseEntityUser();
}
|
消费端测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class FeignDemoConsumerApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ConsumerTypeService consumerTypeService;
@Test
void feignReturnTypeTest() {
Set<String> methodSet = Arrays.stream(Object.class.getMethods()).map(Method::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Method[] methods = ConsumerCollectionTypeService.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (methodSet.contains(method.getName())) {
continue;
}else {
log.info("invoke: {}",method.getName());
Object result = null;
try {
result = method.invoke(consumerTypeService);
log.info("result: {}",result.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("result: {} >>> error!",method.getName());
}
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
}
}
}
|
结果自然是ok的,图就不贴了。
1.2 集合类型
提供端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/collection")
public class ProviderCollectionTyoeController {
private static User admin = new User("admin",18);
@RequestMapping("/list/string")
public List<String> listString() {
return Collections.singletonList("abcdefg");
}
@RequestMapping("/list/user")
public List<User> listUser() {
return Collections.singletonList(admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/set/string")
public Set<String> setString() {
return Collections.singleton("abcdefg");
}
@RequestMapping("/set/user")
public Set<User> setUser() {
return Collections.singleton(admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/map/string/string")
public Map<String,String> mapStringString() {
return Collections.singletonMap("name","zs");
}
@RequestMapping("/map/string/user")
public Map<String,User> mapStringUser() {
return Collections.singletonMap("admin",admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/map/user/user")
public Map<User,User> mapUserUser() {
return Collections.singletonMap(admin,admin);
}
}
|
消费端测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @Test
void feignReturnCollectionTest() {
Set<String> methodSet = Arrays.stream(Object.class.getMethods()).map(Method::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Method[] methods = ConsumerCollectionTypeService.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (methodSet.contains(method.getName())) {
continue;
}else {
log.info("invoke: {}",method.getName());
Object result = null;
try {
result = method.invoke(consumerCollectionTypeService);
log.info("result: {}",result.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("result: {} >>> error!",method.getName());
}
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
}
}
|
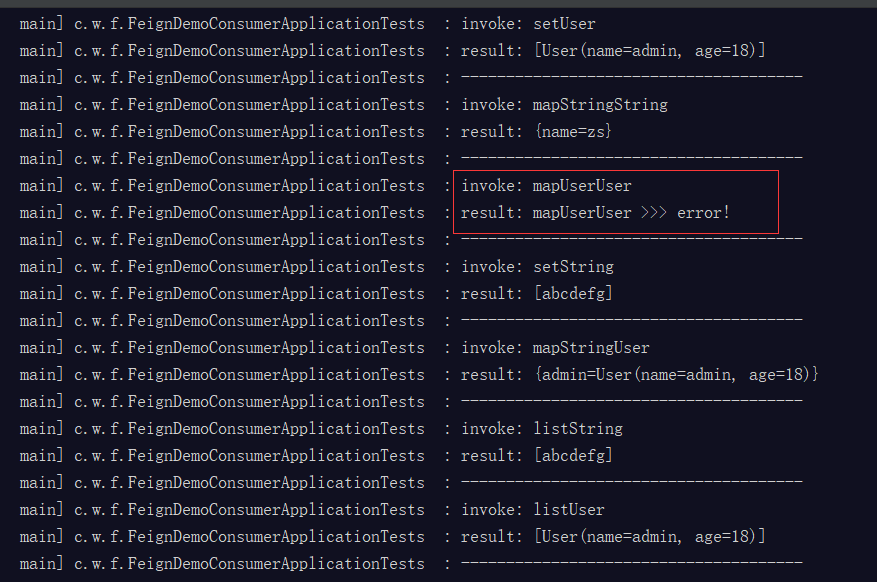
测试结果:
可见接收类型为map类型时,键类型为bean是不可以的;
case2:参数位置不同
提供端web
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/case")
public class ProviderCaseController {
@RequestMapping("/noParams")
public String noParams() {
return "have no params";
}
@RequestMapping("/haveParams")
public String haveParams(String name) {
return "have params " + (name == null ? "null" : name);
}
@RequestMapping("/path/{city}")
public String path(@PathVariable("city") String city) {
return "path " + (city == null ? "null" : city);
}
@RequestMapping("/header")
public String header(@RequestHeader("gender") String gender) {
return "header: " + (gender == null ? "null" : gender);
}
@RequestMapping("/body")
public String body(@RequestBody User user) {
return "body: " + (user == null ? "null" : user.toString());
}
}
|
消费端service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| @FeignClient(name = "consumerCaseService", url = "http://127.0.0.1:8080/provider", path = "/case")
public interface ConsumerCaseService {
@RequestMapping("/noParams")
String noParams();
@RequestMapping("/haveParams")
String haveParams(String name);
@RequestMapping("/path/{city}")
String path(@PathVariable("city") String city);
@RequestMapping("/header")
String header(@RequestHeader("gender") String gender);
@RequestMapping("/body")
String body(@RequestBody User user);
}
|
消费端测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@Test
void feignParamsCaseTest(){
log.info("无参数:{}", consumerCaseService.noParams());
log.info("有参数:{}", consumerCaseService.haveParams("root"));
log.info("参数在path:{}", consumerCaseService.path("北京"));
log.info("参数在header:{}", consumerCaseService.header("女"));
log.info("参数在body:{}", consumerCaseService.body(new User("ls",20)));
}
|
测试结果ok,图就不贴了。
case3:出错情况
提供端web
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/error")
public class ProviderErrorController {
@RequestMapping("/runtimeException")
public String runtimeException() {
throw new RuntimeException("throw RuntimeException");
}
@RequestMapping("/exception")
public String exception() throws Exception {
throw new Exception("Exception");
}
@RequestMapping("/integer/{value}")
public String paramsBindException(@PathVariable("value") Integer value) {
return "Integer param is " + (value == null ? "null" : value);
}
@RequestMapping("/abcdefg")
String request404();
}
|
消费端service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @FeignClient(name = "consumerErrorService", url = "http://127.0.0.1:8080/provider", path = "/error")
public interface ConsumerErrorService {
@RequestMapping("/runtimeException")
String runtimeException();
@RequestMapping("/exception")
String exception();
@RequestMapping("/integer/{value}")
String paramsBindException(@PathVariable("value") String value);
}
|
消费端测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
@Test
void feignErrorTest(){
try {
log.info("提供端运行时异常");
log.info("请求结果:{}",consumerErrorService.runtimeException());
}catch (Exception e) {
log.error("捕获到异常",e);
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
try {
log.info("提供端检查型异常");
log.info("请求结果:{}",consumerErrorService.exception());
}catch (Exception e) {
log.error("捕获到异常",e);
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
try {
log.info("提供端参数绑定异常");
log.info("请求结果:{}",consumerErrorService.paramsBindException("abc"));
}catch (Exception e) {
log.error("捕获到异常",e);
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
try {
log.info("请求不存在的地址");
log.info("请求结果:{}",consumerErrorService.request404());
}catch (Exception e) {
log.error("捕获到异常",e);
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
}
|
测试结果
提供端运行时异常
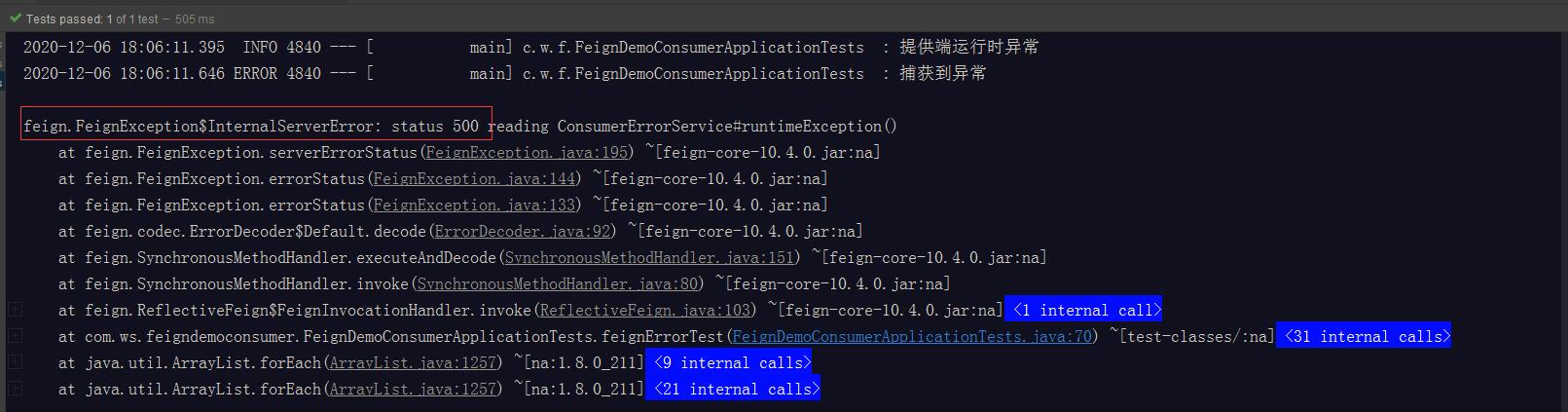
提供端检查型异常(500)
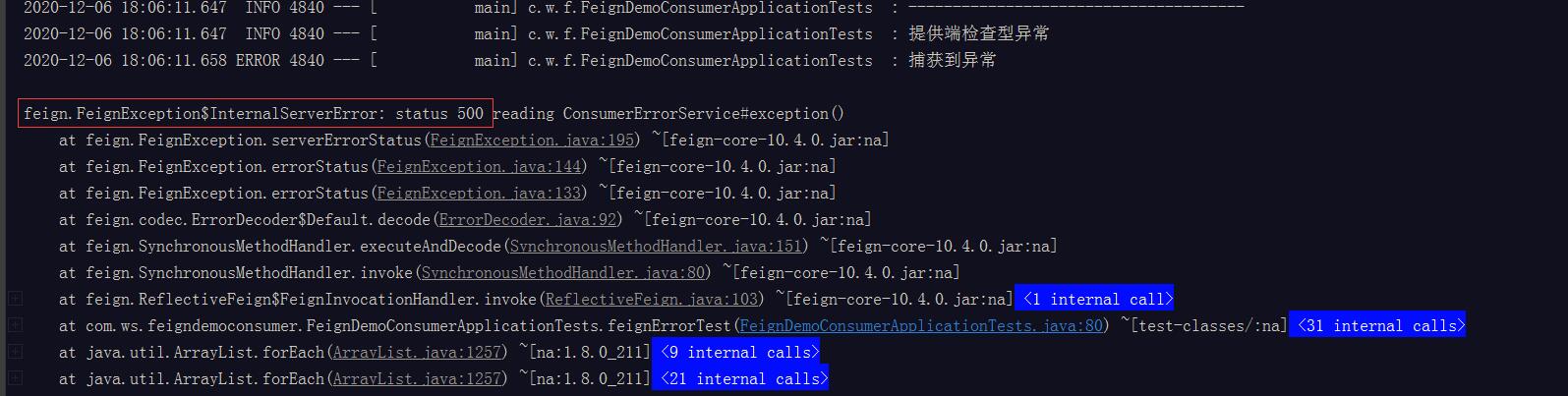
提供端参数绑定异常(500)
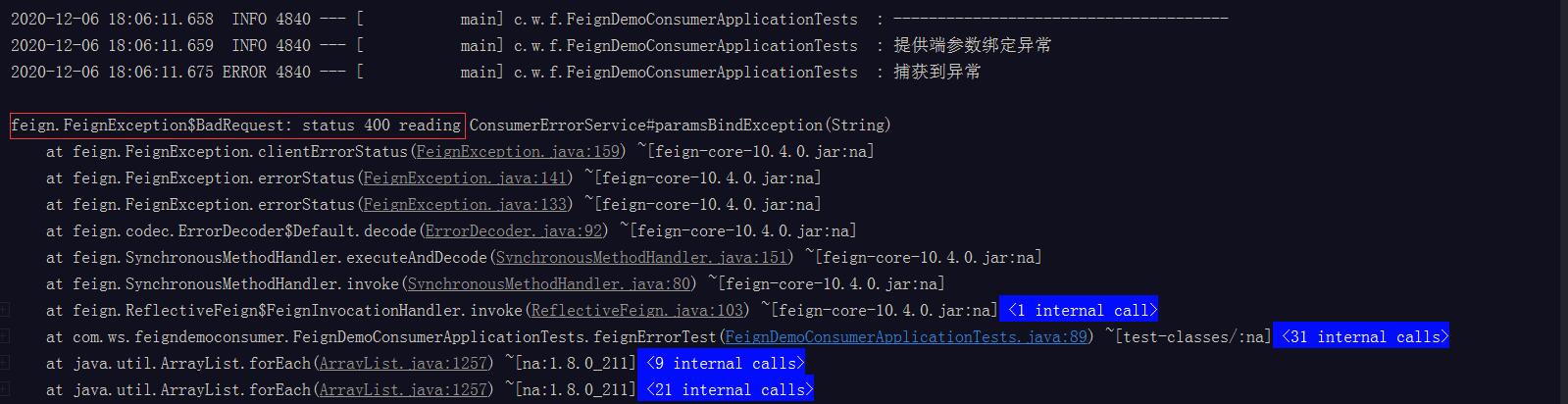
请求不存在的地址(404)
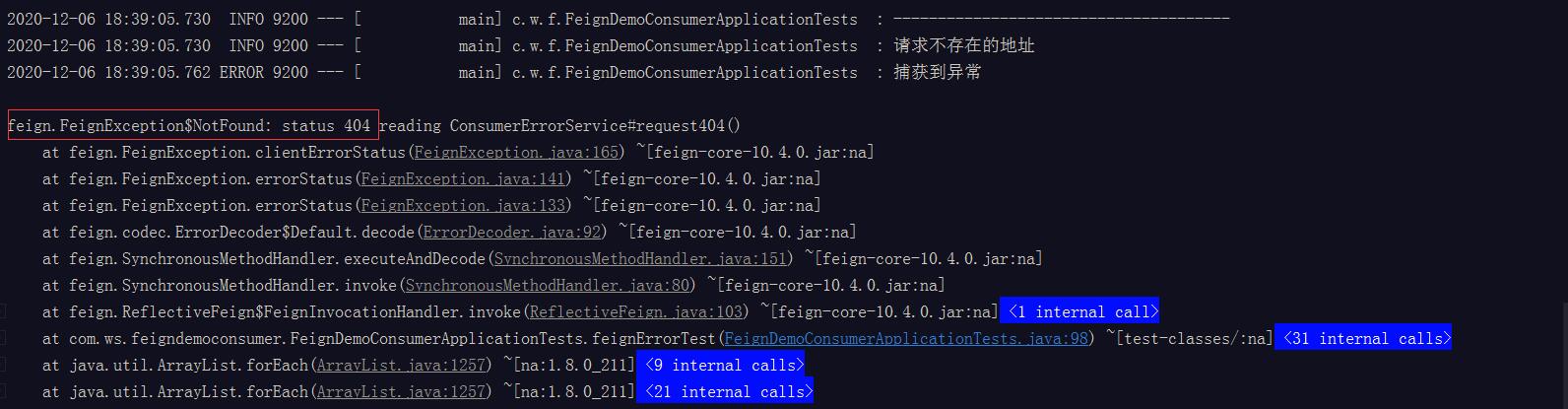
可以看到提供端出现异常时,消费端这边会抛出FeignException的子类异常,异常信息包含了响应码,FeignException的体系如下(部分子类)
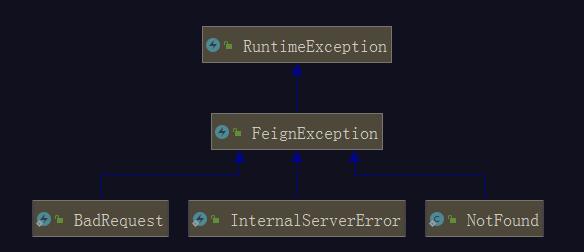
case4:其它情况
4.1 消费端以Object接收
设置新的pojo,内置属性为Object超类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class ObjectResponse {
private String msg;
private Object object;
}
|
提供端web
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| @Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/other/objecttype")
public class ProviderObjectTypeController {
private static User admin = new User("admin",18);
@RequestMapping("/object/string")
public Object returnString() {
return "---------";
}
@RequestMapping("/object/user")
public Object returnUser() {
return admin;
}
@RequestMapping("/object/map/string")
public Object returnMapString() {
return Collections.singletonMap("name","zs");
}
@RequestMapping("/object/map/user")
public Object returnMapUser() {
return Collections.singletonMap("admin",admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/object/set/string")
public Object returnSetString() {
return Collections.singleton("name");
}
@RequestMapping("/object/set/user")
public Object returnSetUser() {
return Collections.singleton(admin);
}
@RequestMapping("/object/objectResponse/string")
public ObjectResponse returnObjectResponseString() {
return new ObjectResponse("msgmsg","abcdefg");
}
@RequestMapping("/object/objectResponse/user")
public ObjectResponse returnObjectResponseUser() {
return new ObjectResponse("msgmsg",admin);
}
}
|
消费端service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| @FeignClient(name = "consumerObjectTypeService", url = "http://127.0.0.1:8080/provider", path = "/other/objecttype")
public interface ConsumerObjectTypeService {
@RequestMapping("/object/string")
Object returnString();
@RequestMapping("/object/user")
Object returnUser();
@RequestMapping("/object/map/string")
Object returnMapString();
@RequestMapping("/object/map/user")
Object returnMapUser();
@RequestMapping("/object/set/string")
Object returnSetString();
@RequestMapping("/object/set/user")
Object returnSetUser();
@RequestMapping("/object/objectResponse/string")
ObjectResponse returnObjectResponseString();
@RequestMapping("/object/objectResponse/user")
ObjectResponse returnObjectResponseUser();
}
|
消费端测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| @Test
void objectTypeTest() {
log.info("响应类型不一致测试");
Set<String> methodSet = Arrays.stream(Object.class.getMethods()).map(Method::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Method[] methods = ConsumerObjectTypeService.class.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (methodSet.contains(method.getName())) {
continue;
}else {
log.info("invoke: {}",method.getName());
Object result = null;
try {
result = method.invoke(consumerObjectTypeService);
log.info("class : {} result: {}",result.getClass(),result.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("result: >>> error! {}",method.getName());
}
log.info("--------------------------------------");
}
}
}
|
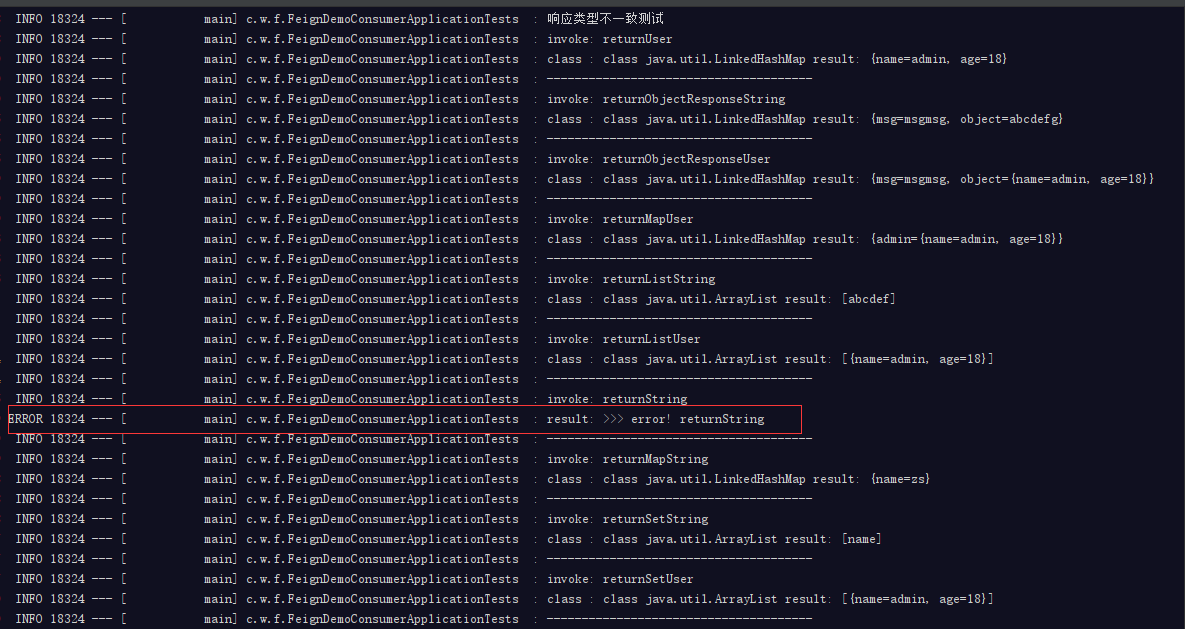
测试结果
以Objec接收String类型时出错;
以Objec接收List、Set类型时,其底层为ArrayList;
以Objec接收Map和其它类型bean时类型时,其底层为LinkedHashMap;
小结
- 在接口上使用
@FeignClient注解即可配置一个Feign的web客户端,接口方法的书写方式可以同控制层写法类似,支持泛型
- 成为Feign的web客户端的接口的方法,在调用时,若服务提供端出现异常,即响应错误类型的响应码,如500、400等,该方法会抛出FeignException,该异常为运行时异常。
- Feign底层使用json序列化传输,使用LinkedHashMap和ArrayList进行存储,上述测试出错的方法张,仔细分析就能发现这些数据是没办法进行反序列化成对于的数据类型的
Feign客户端的写法
SpringMVC式写法
通过demo我们知道作为Feign客户端的接口的方法写法可以和SpringMVC控制层的方法类似,即前者是后者的子集,故而也支持使用REST风格的注解,如@GetMapping等等。服务消费端SpringMVC式写法的传参和服务提供端的取参自然是对应的,不过有一个不一样的地方就是,消费端接口上不能使用@RequestMapping注解来声明前缀,因为@FeignClient注解的 path属性就已经做到了
1
2
3
4
5
| @FeignClient(name = "beanName", url = "http://ip:port/xxx", path = "/prefix")
@RequestMapping("/yyy")
public interface xxxService {
}
|
Feign自带写法
Feign客户单除了mvc式的写法外,还有Feign自带的一种写法,使用@RequestLine注解,注解上使用表达式来声明请求的方式和地址
1
2
3
4
5
| @FeignClient(name = "beanName", url = "http://ip:port/xxx", path = "/prefix")
public interface xxxService {
@RequestLine("GET /xxx/{name}")
String method(@Param("name") String name);
}
|
想要开启这种写法需要加一个配置类,往IOC中加入类型为Contract的bean,该类的实例决定了Feign客户端的写法,Feign默认的写法是“mvc式”,加上下面这个配置后即可使用Feign自带的写法,即使用@RequestLine注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Configuration
public class FeignClientConfig {
@Bean
public Contract feignContract() {
return new feign.Contract.Default();
}
}
|
不仅如此,@FeignClient与配置类的搭配也有讲究,分两种:
配置类加@Configuration注解,则Feign客户端接口使用@FeignClient可以和“mvc式”一样不加其它配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @FeignClient(name = "beanName", url = "http://ip:port/xxx", path = "/prefix")
public interface xxxService {
@RequestLine("GET /xxx")
public String method();
}
@Configuration
public class FeignClientConfig {
@Bean
public Contract feignContract() {
return new feign.Contract.Default();
}
}
|
配置类不加@Configuration注解,则Feign客户端接口使用@FeignClient需要指定配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @FeignClient(name = "beanName", url = "http://ip:port/xxx", path = "/prefix", configuration = FeignClientConfig.class)
public interface xxxService {
@RequestLine("GET /xxx/{name}")
public String method();
}
public class FeignClientConfig {
@Bean
public Contract feignContract() {
return new feign.Contract.Default();
}
}
|
若使用了【1】的配置,即全局配置,则所以的Feign客户端(接口)都必须使用Feign自带的写法。







